Accidents can happen anytime, anywhere, and often when we least expect them. Being prepared and equipped with basic first aid knowledge and skills can make all the difference in an emergency situation. Basic first aid refers to the immediate medical care provided in the event of an injury or sudden illness before professional assistance arrives. Even if you’re not a medical professional, mastering basic first aid can help you save lives, prevent serious injuries, and provide essential care when it’s needed the most.
Key Takeaways
- Basic first aid is essential knowledge that can assist in saving lives.
- First aid knowledge can assist in preventing serious injuries and providing medical care.
- Basic life support, first aid for common injuries, and emergency first aid techniques are important skills to learn.
- Proper training and preparedness can help you perform first aid with confidence and assurance.
The Fundamentals of Basic First Aid
Accidents can happen at any time, so it’s essential to know the basics of first aid. Basic first aid involves simple procedures that can save lives by stabilizing a person’s condition before medical help arrives.
There are several essential first aid skills that everyone should know, including assessing the situation, calling for emergency services, performing CPR and basic life support, stopping bleeding, and treating wounds. These skills are vital in cases of accidents, injuries, and sudden illnesses.
| Basic First Aid Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessing the situation | When an emergency occurs, the first step is to assess the situation and the condition of the person who needs help. Assessing the situation means looking for any potential hazards, determining the severity of the injury or illness, and deciding on the appropriate course of action. |
| Calling for emergency services | If the situation requires emergency medical attention, call 911 or the local emergency services number immediately. Be prepared to provide the address and details of the situation. |
| CPR and basic life support | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving technique that involves chest compressions and rescue breathing. Knowing how to perform CPR and basic life support can mean the difference between life and death in an emergency situation. |
| Stopping bleeding | Stopping severe bleeding is critical in an emergency. Applying pressure to the wound, elevating the injured area, and using a tourniquet (as a last resort) can help stop the bleeding. |
| Treating wounds | Cleaning the wound, applying sterile dressings, and using antibiotic ointment can help prevent infection and promote healing. |
It’s important to remember that basic first aid is not a substitute for medical treatment. In severe cases, it’s vital to call for emergency services and let the professionals handle the situation.
First Aid for Common Injuries
When accidents happen, it’s essential to have the knowledge of basic first aid procedures to deal with common injuries. Knowing what to do can mean the difference between life and death. Here are some of the most common injuries that require first aid and the steps you should take to provide relief:
Bumps, Bruises, and Sprains
Minor bumps and bruises can be treated with ice packs and rest. If the injury is more severe, and you suspect a sprain, remember the acronym RICE. Rest the affected limb, apply Ice to reduce swelling, Compress the area with a bandage, and Elevate it above the heart to reduce pain and discomfort. Seek medical attention if the pain is severe or if the swelling doesn’t go down.
Bleeding
If someone is bleeding, the first step is to apply pressure to the wound. Use a clean cloth or bandage to apply direct pressure to the wound until the bleeding stops. If the bleeding doesn’t stop after 10-15 minutes, call 911 or seek medical attention. In the meantime, keep applying pressure to the wound.
Burns and Scalds
Minor burns and scalds can be treated with cool running water for at least 10 minutes. Remove any jewelry or clothing from the affected area and cover it with a sterile bandage. Seek medical attention if the burn is severe or if it covers a large area of the body.
Choking
If someone is choking, ask them if they need help. If they cannot speak, perform the Heimlich maneuver. Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist. Make a fist with one hand and place it just above the navel. Cover the fist with your other hand and push inward and upward in quick thrusts until the object becomes dislodged.
Remember, basic first aid knowledge can help you provide life-saving aid to someone in an emergency. It’s crucial to stay calm and composed and seek medical attention if an injury is severe or life-threatening.
CPR and Basic Life Support
When someone experiences a cardiac arrest or stops breathing, immediate action is necessary to save their life. This is where CPR and basic life support come into play. These essential first aid techniques involve chest compressions to restore blood circulation and rescue breathing to provide oxygen to the lungs.
The first step in performing CPR is to check for responsiveness. If the person is not responsive, call for emergency medical help immediately. Begin CPR by positioning the person on their back and placing the heel of your hand on their chest. Interlock your fingers and compress the chest at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute, with a depth of 2 inches. After every 30 compressions, provide two rescue breaths by tilting their head back and pinching their nose while blowing into their mouth for about one second.
It’s essential to remember that CPR and basic life support are physically demanding, especially if performed for an extended period. Therefore, it’s vital to switch with another person between cycles to avoid fatigue. Basic life support also includes the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) to deliver an electric shock to the heart in case of a cardiac arrest.
Hands-Only CPR
Hands-only CPR is just as effective as traditional CPR at saving lives, and it is easier to learn and perform. If you are not comfortable giving rescue breaths, you can still help someone in cardiac arrest by doing hands-only CPR.
Hands-only CPR involves giving chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. The chest compressions should be deep enough to compress the chest by at least 2 inches (5 centimeters).
Dealing with Burns and Scalds
If you or someone else suffers from burns or scalds, it is important to provide first aid as soon as possible. This can help to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of infection. Follow these basic first aid procedures to successfully provide care for the affected area.
1. Cool the burn or scald
The first step to treating a burn or scald is to cool the affected area. Hold the burned area under cool (not cold) running water for about 10 minutes, or until the pain subsides. If cool water is not available, you may use a clean, damp cloth to gently cool the area.
2. Remove clothing and jewelry
If clothing or jewelry is stuck to the burned skin, do not attempt to remove it. However, if they are not stuck, carefully remove them from the affected area to prevent further damage if swelling occurs.
3. Cover the burn or scald
Once the burned area has been cooled, cover it with a sterile, non-adhesive dressing, or a clean, non-fluffy material. Do not use any kind of cream, lotion, or ointment on the area, as this can increase the risk of infection.
4. Seek medical attention
If the burn or scald is large, covers a major joint, is on the face, hands, feet or genitals, or if it is accompanied by severe pain, difficulty breathing, or signs of shock, seek medical attention immediately. These are all indications that the burn or scald may be more severe than initially thought.
Remember, knowing basic first aid procedures for burns and scalds can help you respond quickly and effectively in an emergency situation. Keep these tips in mind and be prepared to provide essential care when needed.
Handling Choking Emergencies
Choking can be a scary experience, but knowing how to respond quickly and correctly can potentially save someone’s life. If someone is choking, they may be unable to speak or breathe, and their face may turn blue or red. Here are the steps to follow in a choking emergency:
- Assess the situation – if the person is coughing, encourage them to continue coughing and monitor them closely. If they are not coughing and cannot speak or breathe, they need immediate assistance.
- Perform the Heimlich maneuver – stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist. Make a fist with one hand and position it above the person’s belly button. Grasp your fist with your other hand and give quick upward thrusts into their abdomen until the object is dislodged.
- If the person is pregnant or obese, position your hands higher up on their chest and perform chest thrusts instead.
- If the person becomes unconscious, carefully lower them to the ground and begin CPR immediately.
- Call for emergency medical assistance if the person remains unconscious or if you are unable to dislodge the object.
It’s important to note that choking can happen to anyone, so it’s essential to know the proper procedures for handling this type of emergency.
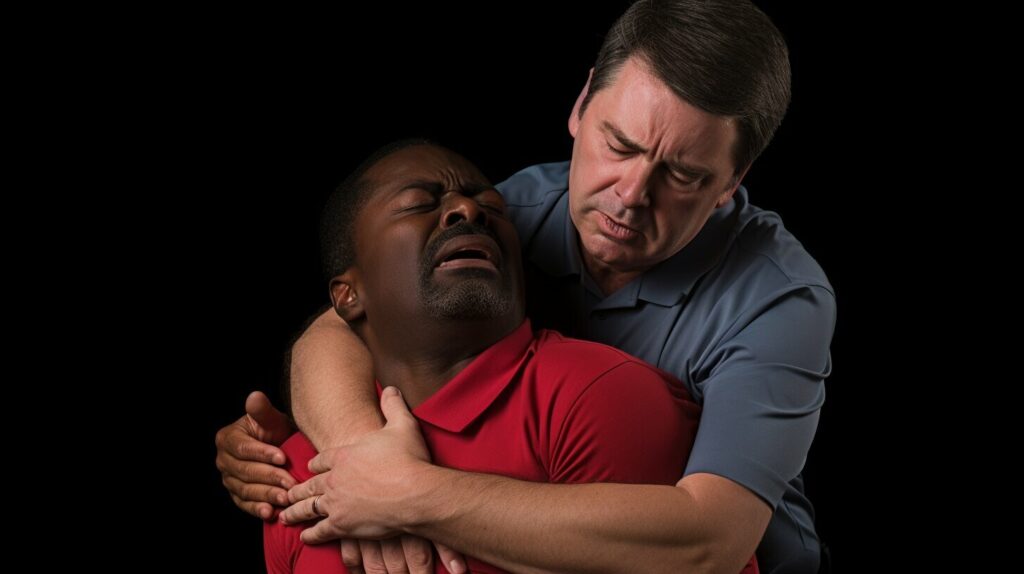

Remember to remain calm and act quickly in a choking emergency. By following these basic first aid procedures, you can potentially save someone’s life.
Treating Bleeding and Wounds
Injuries that result in bleeding and open wounds can be scary, but knowing how to properly address them can make a significant difference in the outcome. Follow these basic first aid procedures to provide initial care for bleeding and wounds:
| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1 | Apply direct pressure |
| 2 | Elevate the affected area |
| 3 | Apply a clean dressing |
| 4 | Monitor for signs of infection |
The first step in providing first aid for bleeding and wounds is to apply direct pressure to the affected area. If there are any objects in the wound, do not remove them. Instead, use a clean dressing or cloth to cover the wound and apply pressure to control the bleeding.
The second step is to elevate the affected area above the heart level to minimize blood loss.
Once the bleeding is under control, apply a clean dressing to the wound. For minor lacerations, use adhesive bandages. For larger wounds, use sterile gauze and secure it with adhesive tape.
Finally, monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or drainage. Seek medical attention if these signs develop or the wound does not heal properly.
By following these basic first aid procedures for bleeding and wounds, you can provide essential care and help prevent further injury.
Managing Fractures and Sprains
If you or someone you know suffers from a fracture or sprain, quick action can help minimize the injury and prevent further damage. It is important to have a basic understanding of basic first aid procedures to handle these injuries effectively.
A fracture happens when a bone is cracked or broken. If you believe that someone might have a fractured bone, keep them immobile and support the weight of the affected limb.
For sprain, gently support the affected area and apply ice packs to minimize swelling. Immobilize the affected limb and keep it elevated to reduce pain and swelling.
It is important to seek professional medical help as soon as possible, but effective first aid procedures help to minimize the injury until further medical attention is available.
| Fractures | 1. Keep the affected limb immobile and support the weight. 2. Cover the affected limb with ice to reduce pain and swelling. 3. Seek professional medical help as soon as possible. |
|---|---|
| Sprains | 1. Apply ice to the affected area. 2. Gently support the affected area. 3. Immobilize the affected area and keep it elevated. 4. Seek professional medical help as soon as possible. |
Following these basic first aid procedures can help minimize the injury and prevent further damage. However, it is important to seek prompt medical attention for more severe fractures and sprains. Remember, learning essential first aid skills is crucial in handling emergencies.
Conclusion
Now that you have learned about basic first aid, emergency first aid, and essential first aid skills, you are better equipped to handle common injuries and potentially life-threatening situations.
Remember to always prioritize your safety and the safety of those around you. By mastering basic first aid techniques and procedures, you can provide basic medical care and potentially save lives.
Make sure to keep a first aid kit readily available and updated with essential supplies. Practice your skills regularly to ensure that you can act quickly and confidently in an emergency.
By taking the time to learn about basic life support, first aid for common injuries, and first aid tips and instructions, you can make a difference in the lives of those around you. Stay prepared and stay safe.
FAQ
Q: What is basic first aid?
A: Basic first aid refers to the immediate medical care and assistance provided to a person who is injured or suddenly becomes ill. It includes simple techniques and procedures that can be performed with minimal equipment and training.
Q: Why is it important to learn basic first aid?
A: Learning basic first aid is crucial because it enables you to respond effectively to emergencies and potentially save lives. By knowing how to handle common injuries and illnesses, you can provide immediate care until professional medical help arrives.
Q: What are some essential first aid skills to learn?
A: Some essential first aid skills include CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), managing bleeding and wounds, treating burns and scalds, handling choking emergencies, and immobilizing fractures and sprains. These skills can greatly increase the chances of a positive outcome in an emergency situation.
Q: How can I administer CPR and basic life support?
A: To administer CPR and basic life support, you should start by checking the person’s responsiveness and breathing. If they are unresponsive and not breathing, you should perform chest compressions and rescue breaths according to the guidelines provided by organizations like the American Heart Association.
Q: How should burns and scalds be treated?
A: Burns and scalds should be treated by immediately cooling the affected area with running water for at least 10 minutes. It is important to remove any clothing or jewelry that is not stuck to the burn. If necessary, cover the burn with a sterile non-stick dressing or clean cloth.
Q: What should I do if someone is choking?
A: If someone is choking, you should encourage them to cough to try and dislodge the object. If that doesn’t work, you can perform the Heimlich maneuver by standing behind the person and giving quick upward thrusts to their abdomen. Back blows can also be used to dislodge the object.
Q: How do I treat bleeding and wounds?
A: When dealing with bleeding and wounds, it is important to apply pressure to the area using a clean cloth or your hand. Elevating the injured limb, if possible, can help reduce bleeding. Clean the wound with mild soap and water, and apply a sterile bandage to protect it.
Q: How do I manage fractures and sprains?
A: When managing fractures and sprains, it is important to immobilize the affected area using a splint or sling. Applying ice packs wrapped in a cloth can help reduce swelling and pain. Seek medical attention as soon as possible to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.